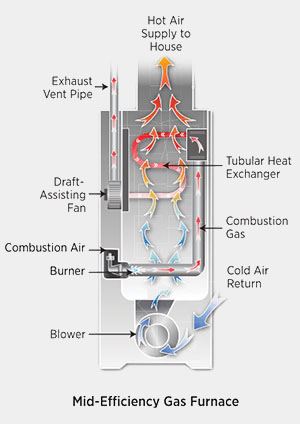
Mid-Efficiency Furnaces (80% to 82%)
Mid-efficiency (80% to 82%) furnaces have no draft hood. Instead, they use fan-assisted draft with a fan located at the outlet (draft inducer) of the heat exchanger to create a regulated flow of combustion air. This design change increased efficiency from 65% AFUE in atmospheric draft furnaces to over 80% in fan-assisted furnaces. Fan-assisted draft minimizes the risk of backdrafting.
How to Find Efficiency of Furnace
For furnaces with an oil burner, one way to determine the age and efficiency is to look at the nameplate.
- If the oil furnace has a nameplate motor speed of 1,725 rpm, it is most likely an older model with a less efficient burner.
- Models with a nameplate motor speed of 3,450 are newer than 20 years old and have a flame retention burner that wastes less heat; they have a steady-state efficiency of 80% or more.
Bigger isn’t Always Better
Many older furnaces and central air conditioning systems are oversized. An energy performance contractor can run energy analysis software to help you determine your heating and cooling needs after air sealing and insulation improvements are made
How to Calculate Furnace Size
In the past, many HVAC contractors used “rules of thumb” to determine HVAC sizing and, as a result, many installed oversized systems. Today’s trained HVAC contractor should determine your heating and cooling loads, and the right size for your HVAC equipment, based on calculations developed by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA 2005; 1995; 2009).




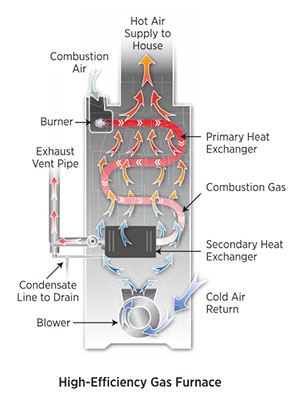
High-Efficiency Furnaces (90% to 98%)
The most efficient furnaces available today are sealed-combustion (direct-vent) condensing furnaces, which have efficiencies of 90% to 98%.
What Is a High Efficiency Condensing Furnace?
About 12% of the heat from the combustion process is captured in water vapor as latent heat. A condensing furnace condenses this water vapor through a secondary heat exchanger to capture the heat rather than letting it escape up the flue.
This technological advance enabled gas furnaces to jump from 82% AFUE to 90% AFUE or higher (ACEEE 2011). There are no gas furnaces with AFUE ratings between 83% and 89% because of problems arising from condensation in the heat exchangers that occur within this range.
How Do Condensing Gas Furnaces Work?
High-efficiency condensing furnaces avoid back-drafting issues by having sealed combustion. These furnaces are designed to vent exhaust gases (combustion products) directly to the outside through a dedicated vent pipe. They should also be installed with a second vent pipe to bring outside air directly into the combustion chamber.
Condensing Furnace vs. Non-Condensing Furnace
Although a condensing unit costs more than a non-condensing unit, the condensing unit will save money in fuel costs over its 15- to 20-year life and is a particularly wise investment in cold climates.
AFUE Ratings of Combustion Furnaces
Nearly all combustion furnaces sold today meet or exceed 80% AFUE. About one-third of current sales on a national basis are 90% AFUE or better. In just the past 10 years alone, about 7.5 million condensing furnaces went into replacement installations in the United States (ACEEE 2011)
AFUE Ratings of Electric Resistance Furnaces
The AFUE rating for an all-electric resistance furnace or boiler is between 95% and 100%; because there is no combustion, no heat loss occurs up the flue, but there may be some heat loss through the furnace housing. However in some parts of the country, electricity is expensive to purchase and it can be expensive to produce from an environmental standpoint as well, making electric heat a less cost- effective option.
Options Available
Both mid- and high–efficiency furnaces are available with two-stage gas valves, two-speed draft fans, and variable-speed blower fans, which reduce their electricity usage by better matching air flow rate to the heating needs of the home.
-
“We will use Precision and Kevin again should any issues arise with our unit.” - Jay B.

schedule Service
Our team is here to answer your questions. Contact us today at (512) 379-6385 or complete the form below.